
Careers
Best 10 Chemicals in Chemistry You Should Know?
Chemistry is a fascinating field. It explores the world of chemistry chemicals that shape our lives. Renowned chemist Dr. Emily Carter once said, “Understanding the fundamental chemicals is key to innovation.” Her insight highlights the importance of certain chemicals in both everyday life and advanced scientific research.
Among the best-known chemistry chemicals are water, carbon dioxide, and hydrochloric acid. Each plays a critical role in various processes. Water is essential for life. Carbon dioxide is vital for photosynthesis. Hydrochloric acid aids in digestion and laboratory experiments.
However, not all chemicals are harmless. Some can be hazardous if not handled properly. Learning about these chemicals requires responsibility and caution. Understanding their properties helps in safe usage. As we dive into the top ten chemicals, we recognize their significance and potential pitfalls.

Overview of Essential Chemicals in Chemistry
Chemistry is a vast field, bursting with essential chemicals that shape our understanding of the world. Water, H₂O, is perhaps the most crucial. It covers 71% of our planet. Water isn't just for drinking. It's a medium for countless reactions. Interestingly, despite its abundance, only about 2.5% of Earth's water is freshwater.
Another integral chemical is carbon dioxide, CO₂. It plays a significant role in photosynthesis. This process helps plants convert sunlight into energy. Notably, data from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change indicates that CO₂ levels have risen sharply since the Industrial Revolution. This rise impacts our climate and ecosystems.
Ammonia, NH₃, is essential in agriculture. It’s a key ingredient in fertilizers. Studies show that nitrogen fertilizers can boost crop yields significantly. However, overuse causes pollution and ecological imbalances. An estimated 1.5 billion tons of nitrogen from fertilizers enter ecosystems annually, causing harmful algal blooms.
Sodium chloride, or table salt, is another chemical of great importance. Beyond flavoring food, it maintains fluid balance in the body. Yet, high salt intake is linked to hypertension and heart disease. The World Health Organization recommends limiting daily salt intake to 5 grams. Balancing chemical use is crucial for health and sustainability.
The Role of Water: The Universal Solvent
Water is often called the universal solvent. This is not mere speculation. Its unique properties allow it to dissolve a wide variety of substances. From salts to sugars, many compounds dissolve easily in water. This characteristic plays a crucial role in nature and biology.
In our daily lives, we witness water's ability to support life. Cells, the building blocks of all living things, rely on water to function. Without it, many biological processes would cease. However, it’s important to acknowledge that not all substances are easily dissolved. Some molecules exhibit resistance to solvation. This can lead to complications in both scientific experiments and natural processes.
In the lab, the choice of solvents can significantly affect reactions. Water may not always be the best choice for every reaction. Sometimes, alternative solvents need consideration. Choosing the right solvent is key to achieving desired results. Understanding the limitations of water expands our appreciation for its role in chemistry and life itself.
Water: The Universal Solvent
Carbon Compounds: The Building Blocks of Life
Carbon compounds are essential for life. They form the basis of all biological molecules. Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids all contain carbon. According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, about 99% of the mass of living organisms comes from six elements, primarily carbon. This makes understanding carbon chemistry vital for studying life itself.
Carbon’s versatile bonding properties allow it to form chains, rings, and complex structures. For example, glucose—a simple sugar—plays a significant role in cellular energy. A research paper published in "Nature" stated that over 70% of human bodies’ dry mass comes from carbon-based compounds. However, the complexity of these structures can lead to challenges in research.
Learning about these compounds is not just academic. It has real-world implications. The increasing prevalence of synthetic organic compounds raises concerns about environmental impact. Scientists report that some carbon compounds contribute to pollution. While they are building blocks of life, they also create challenges. Balancing benefits and risks is ongoing. Exploring carbon’s dual nature fosters a deeper understanding. It sparks innovation while provoking necessary reflection on its role in sustainability.
Best 10 Chemicals in Chemistry You Should Know - Carbon Compounds: The Building Blocks of Life
| Chemical Name | Chemical Formula | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methane | CH4 | 16.04 | Fuel, production of hydrogen |
| Ethanol | C2H5OH | 46.07 | Solvent, fuel, antiseptic |
| Glucose | C6H12O6 | 180.18 | Energy source, sweetener |
| Acetic Acid | C2H4O2 | 60.05 | Food preservative, chemical reagent |
| Benzene | C6H6 | 78.11 | Solvent, starting material for synthesis |
| Formaldehyde | CH2O | 30.03 | Preservative, disinfectant |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | NaHCO3 | 84.01 | Baking, antacid |
| Cholesterol | C27H46O | 386.65 | Cell membrane component |
| Acetone | C3H6O | 58.08 | Solvent, nail polish remover |
| Citric Acid | C6H8O7 | 192.13 | Food additive, preservative |
Acids and Bases: Understanding pH and Chemical Reactivity
Acids and bases play a crucial role in chemistry. Their reactivity impacts numerous processes around us. Understanding pH is vital for scientists and manufacturers alike. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Acids have a pH less than 7, while bases exceed 7. A report by the National Center for Biotechnology Information highlights that even slight changes in pH can significantly affect chemical reactions.
The behavior of acids and bases is fascinating. Strong acids, like hydrochloric acid, can dissolve metals, while weak acids, such as acetic acid, are common in food. Bases can neutralize acids, creating salts and water. However, the handling of strong acids requires extreme care. Accidental exposure can lead to severe damage. Data from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration shows that workplace accidents involving acids cause numerous injuries annually.
Chemists often struggle to accurately measure pH in real-time. This challenge can lead to inconsistencies in research and applications. Developing better pH meters and more precise indicators remains essential. Utilizing pH-sensitive materials could enhance chemical monitoring. As science advances, the need to understand the reactivity of acids and bases will only grow, fostering innovations across various fields.
Metals and Alloys: Key Elements in Industry and Technology
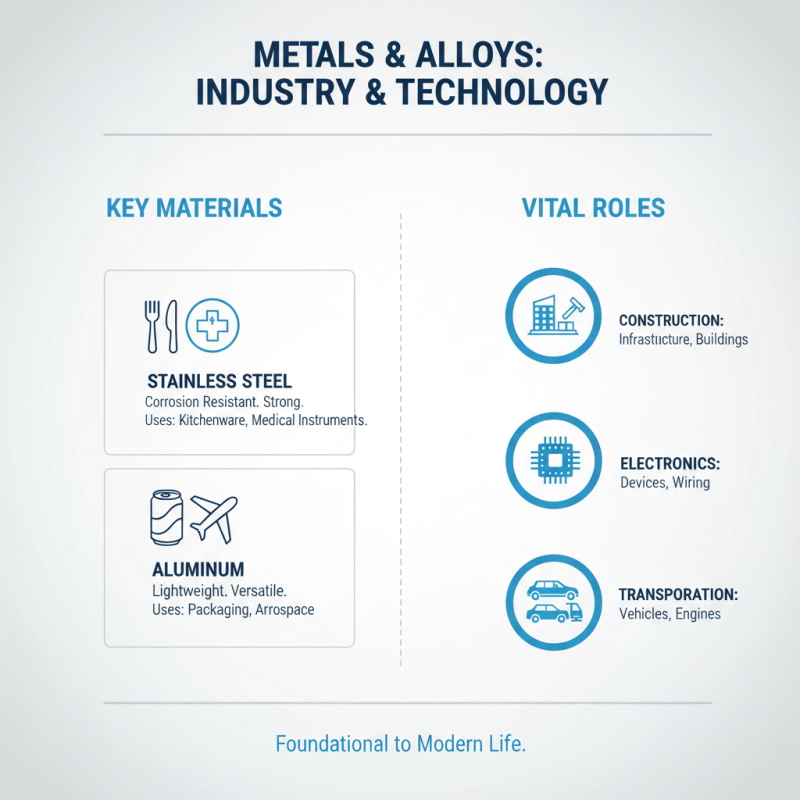
Metals and alloys play a vital role in both industry and technology. These materials are foundational in construction, electronics, and transportation. Stainless steel, for instance, demonstrates corrosion resistance and strength. It's commonly used in kitchen appliances and medical instruments. Aluminum, on the other hand, is lightweight and ideal for packaging materials.
When considering materials for a project, think about their properties. Conductivity, weight, and strength can greatly affect performance. For example, copper is an excellent conductor but is heavier. This can be a disadvantage in certain applications. Aim to balance these variables for the best result.
Tips: Always research the specific requirements of your project. Don’t overlook the importance of alloy composition. A small change can lead to significant differences in performance. Keep in mind that not all metals are equally recyclable. Understanding this can help make better environmental choices.
Related Posts
-
Top 10 Essential Chemicals You Need to Know for Everyday Use
-

How to Optimize Chemical Manufacturing Processes for Increased Efficiency
-

How to Choose the Best Chemical Products for Your Business in 2025
-

10 Essential Tips for Safely Handling Chemistry Chemicals in the Lab
-

Top 10 Essential Chemical Products for Everyday Use?
-

How to Choose and Use High Purity Chemicals for Your Experiments


